Back to October 2025 Industry Update
October 2025 Industry Update: Reefer
The reefer sector remains the most stable of the three major mode types, propping up produce and raising demand for temperature-sensitive commodities amidst cooling weather.
Spot Rates
Key Points
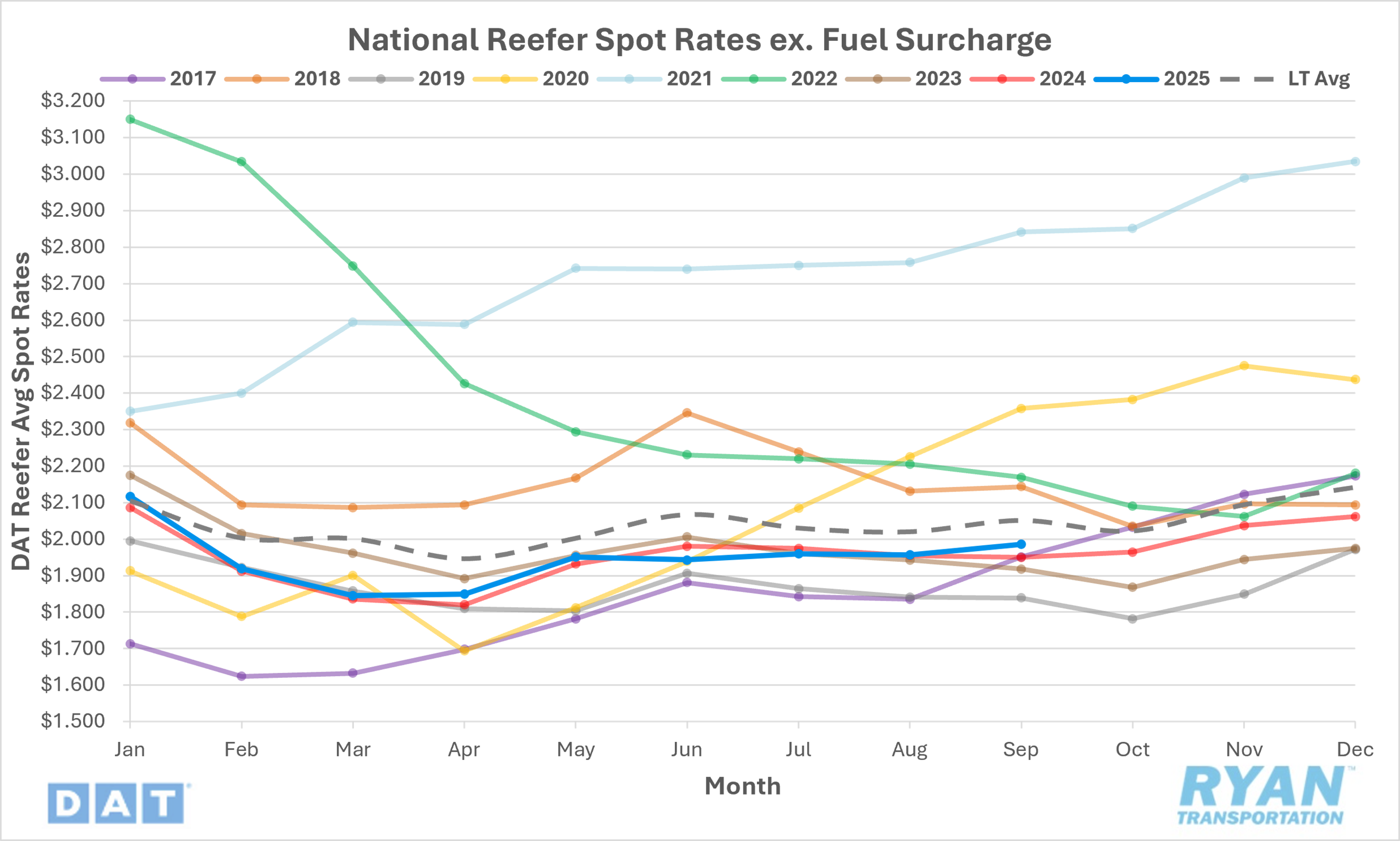
- The national average reefer spot rate, excluding fuel, rose 1.5% MoM, or roughly $0.03, in September to $1.99.
- On an annual basis, average reefer linehaul rates were up 1.8% YoY but were 3.8% below the LT average.
- Initially reported average reefer contract rates, absent a fuel surcharge, rose 0.8% MoM in September and were 0.3% above September 2024 levels.
Load-to-Truck Ratio
Key Points
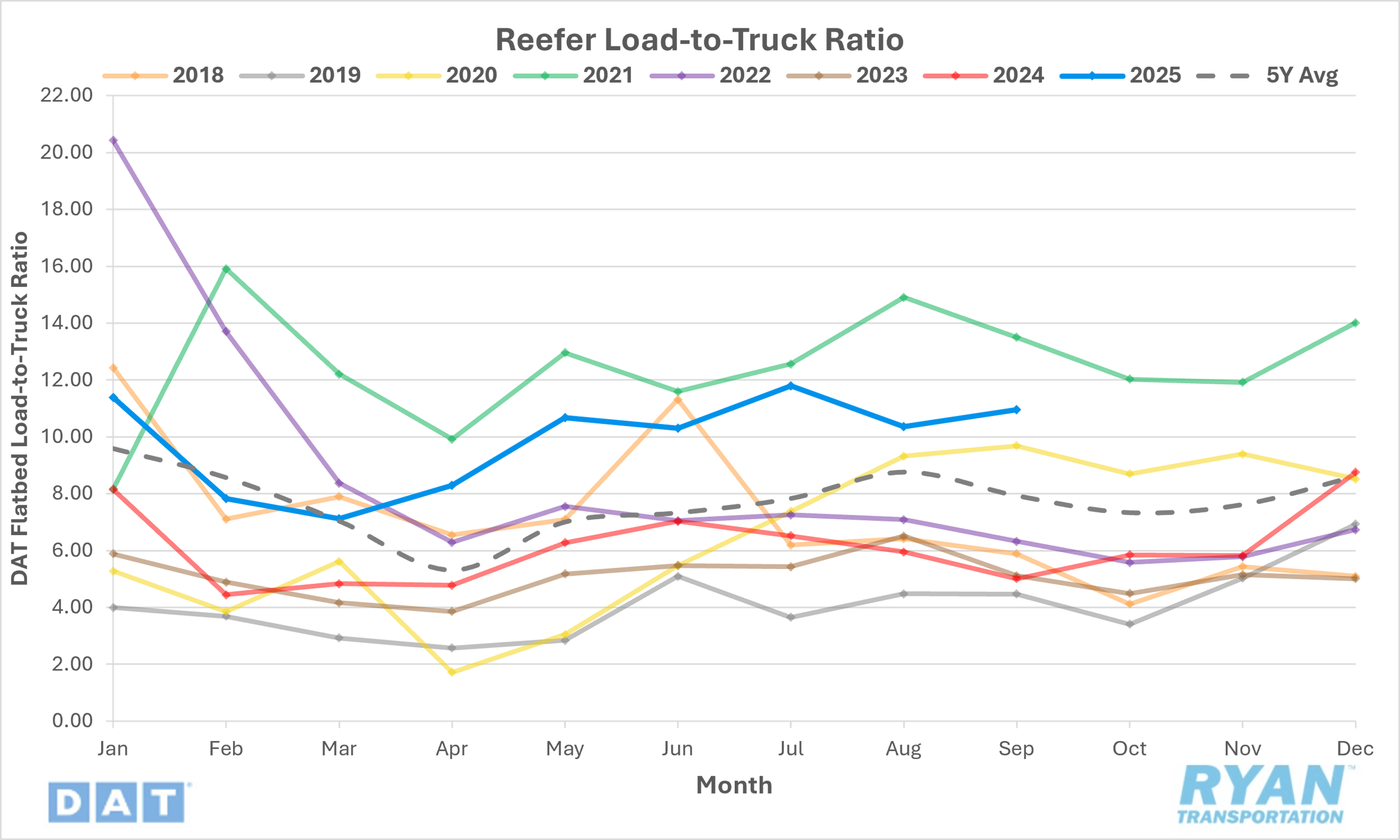
- The reefer LTR increased 5.7% MoM, rising from 10.36 in August to 10.95 in September.
- Compared to September 2024, the reefer LTR was 118.6% higher YoY and is 38.2% above the 5-year average.
- DAT load board data for September recorded a 4.1% MoM increase in refrigerated load posts, while equipment posts were down 1.5% MoM.
Market Conditions
Reefer Summary
The U.S. food and restaurant sectors are facing persistent cost inflation, labor shortages and changing consumer behaviors that are directly influencing refrigerated freight demand. Food prices have climbed 21% over the past four years, outpacing broader inflation, while tariffs and labor shortages are compounding operational pressures. Consumers are becoming increasingly cautious, with both low- and middle-income households trading down or eating out less. This reduced dining demand has weighed on restaurant sales and shipment volumes, signaling broader consumer restraint. Although some regions such as New York City maintain stronger restaurant activity, overall foodservice freight remains under pressure due to softening consumer demand and margin compression across the industry.
Agricultural activity, particularly in potato, apple, raspberry and sweet potato markets, is creating regional demand spikes. Washington and Oregon expect slightly lower potato shipments due to reduced processed demand, while the apple harvest season (August–October) in New York is significantly tightening reefer capacity, pushing Albany market outbound rates up by 22% in a week. Similarly, North Carolina’s sweet potato harvest — responsible for over one billion pounds annually — drives intense seasonal demand increases during the pre-Thanksgiving period. Raspberry freezing operations in Washington highlight how specialized reefer transport remains critical for maintaining freshness and quality. These cyclical harvest patterns underscore the importance of anticipating capacity surges, especially as holiday seasons approach and temperature-controlled freight becomes more constrained.
The reefer market overall remains relatively stable compared to dry van and flatbed, buoyed by steady food and pharmaceutical shipments. However, softening demand in beverage and discretionary perishables is limiting rate growth. Carriers face rising input costs from fuel, equipment and maintenance, while shippers resist rate increases amid cost-consciousness. Pricing is expected to stay largely flat through the end of 2025, with any upward movement dependent on holiday-driven freight and broader economic recovery. Tariff-driven cost pressures, consumer caution and regulatory uncertainty — particularly around EPA 2027 standards — will continue to weigh on the sector’s outlook through early 2026.